
Textured hair, an untapped territory
The global haircare is estimated to reach over 100,000 million USD of retail value by 2026, which represents a 6.9% year-on-year growth when it is currently valued at 83,363 million USD - according to Euromonitor (figures 2022). In order of importance, shampoo, conditioners and treatments are the most important categories, followed by salon professional haircare, which is expected to grow the fastest on its current trajectory.

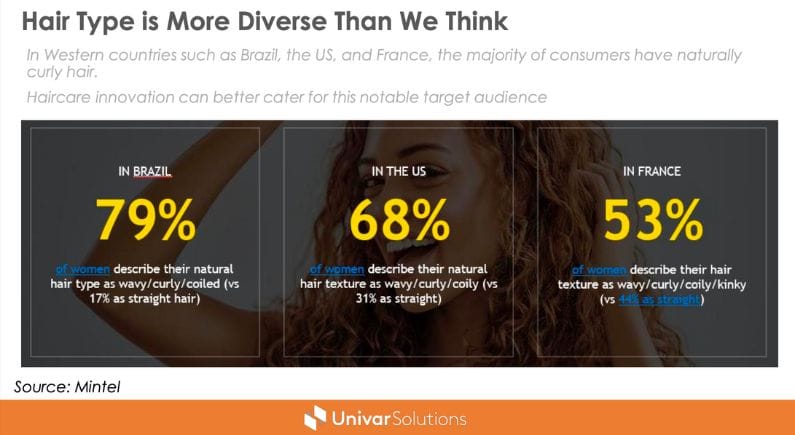
Hair Type is more diverse than we may think. In Western countries such as Brazil, the US, and France, the majority of consumers have naturally curly hair. As an illustration, 79% of women in Brazil describe their natural hair type as wavy, curly and/or coiled compared to 17% claiming to have straight hair. In the US, the first type represents 68% of women and 53% in France. These figures indicate the potential growth of the hair care segment in the market.
We believe that hair care innovation can better cater for this notable target audience.
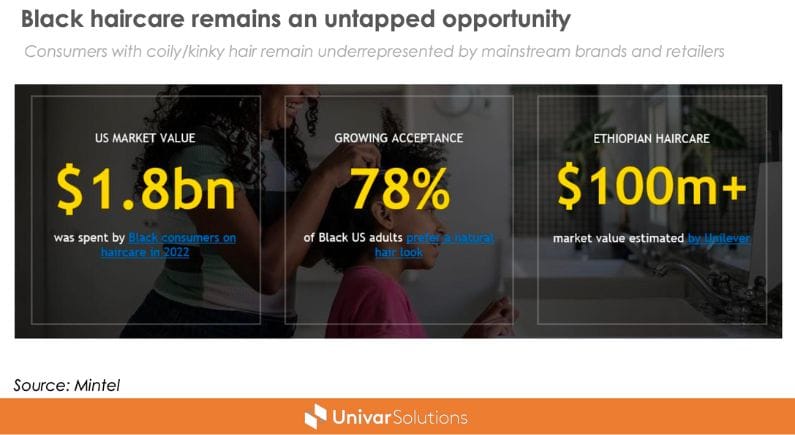
In a similar idea, black hair care has also a strong growth potential and it is estimated at a value of 1.8B$ in the US only in 2022 (consumers spent), with a stronger acceptance for natural hair look - by 78% of surveyed consumers among black American adults (US).
According to Mintel & Spate, the online search for the words “textured hair” hair increased consistently over the last 3 years, and is expecting to reach a 16.7% growth in search criteria over the 12 months of the year 2023. Top google search queries includes the words “textured hair” “textured hair men” or “short textured hair” for example.
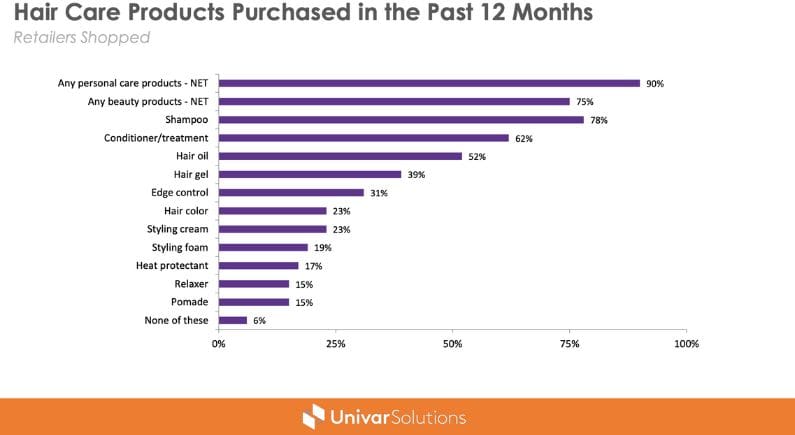
Among the many products on the market the highest growth and consumers purchases were on hair oil (52%), hair gel (39%) and edge (31%) control after traditionally used shampoo and conditioner, in 2022, reported a retailer shoppers survey in the US. More than half (56%) of consumers buying in stores reported buying most of their haircare product at mass merchandiser (i.e: Walmart), when 39% buy at beauty chain store.
Looking at the science of hair
Hair morphology
The main constituent of hair is the protein keratin. Keratin is a remarkable protein which is resistant to wear and tear. It is the protein that makes up feathers, claws, nails and hoofs, as well as hair. Like other proteins, it is made up of smaller units called amino acids, joined together in chains like beads on a string.
Hair contains water which, although it makes up only 10-13% of the hair, is extremely important for its physical and chemical properties. Hair also contains fats, pigment (melanin), small amounts of vitamins, and traces of zinc and other metals.

Hair Shaft Structure: there are three layers of hair shaft
The cuticle is the outer layer.
Outermost layer consists of tiny, transparent overlapping cells resembling scales on a fish or shingles on the roof of a house. The cuticle layer points toward the end of the hair shaft. It is made up of between six and ten overlapping layers of long cells.
The cortex is the middle and largest layer
It lies below the cuticle layer. It represents the majority of the hair shaft. As a result, it is the most important. It is the cortex that gives hair its special qualities such as elasticity. strength and curl. It contains the bonds that are responsible for the hair shape. It also contains pigment granules that give hair its color. This is the layer cosmetologists are most concerned with.
The medulla is the innermost layer
It is the innermost portion of the hair shaft. It can run from root to end; but sometimes only exists in the root. Its function is not known. There are medullae in the hairs of many animals, and they play a part in the regulation of body temperature. It may be that the presence of this air space in some human hairs is an evolutionary 'throw-back' to a time when our ancestors needed extra heat insulation.

Hair shaft
This is the part of the hair that can be seen above the scalp. It consists mainly of dead cells that have turned into keratins and binding material, together with small amounts of water.
Terminal hairs on the head are lubricated by a natural oil (sebum) produced by the sebaceous glands of the follicles
Hair can be compared to a tree: all its moisture lies in its centre, behind a tough outer layer of protective bark. If the 'bark' of the hair is well looked after the whole hair remains in good condition. If the 'bark' is stripped off to expose the centre the hair may break.
Three Main Hair Types

Asian
Hair is very straight, and always black in colour. The diameter of the hair is greater than other hair types and very round or circular in cross section. Asian hair is on average the thickest and most coarse. The density of Asian may be just 90,000 scalp follicles and rarely gets above 120,000 scalp follicles
Caucasoid
Caucasian hair can be quite variable being straight, wavy or curly and the hair diameter varies widely. The fibre is typically oval in cross section and is on average thinner than Asian hair. Hair follicle density varies and density can be approximately related to hair color. Red haired people have the least dense scalp hair growth of Caucasians, blonds the most dense and brown haired people somewhere in the middle. Density can range from 100,000-150,000 scalp hair follicles
African
Hair is black and tightly curled or spiralled. It tends to be dry and unevenly coated with natural sebum. It is easily damaged by heat or chemicals. In the cross section it is elliptical or almost flat and ribbon-like in some cases. This means that the hair is stronger and more rigid across the area of the greatest cross section and more pliable across the narrow section. The scalp hair density is similar as found in Caucasians.
Textured hair needs are very different from the often advertised general market.
Textured Hair tends to be weaker and drier and requires a stronger daily regimen. Shampoo should be done weekly or bi- weekly, and should use mild surfactants. The hair texture need more conditioning (ex. leave-in) and more substantive styling products (silicones, oils, heavier emollients) and Combing can prove hard to detangle hair. Also the hair structure being more porous, more product is needed in application.

In opposition, the hair as promoted in the general market tend to be stronger, more oily and require a lighter/easier daily regimen that is easier to apply. Shampoo cna be done daily or every other day, and offer more cleansing and less conditioning. The hair structure also needs less substantive styling products (lighter oils/emollients, etc.) as combing is proven easy to detangle and hair less porous.
Solutions for Textured Hair
Amongst the hair care solutions, Univar Solutions Beauty and Personal Care has concocted specific recipes for textured hair:





